Self-training exercises#
Question 1#
In our laboratory you will not use the distance measurements. There is a tool for this, called linear variable differential transformer (LVDT).
Read and summarize the principle of action of LVDT
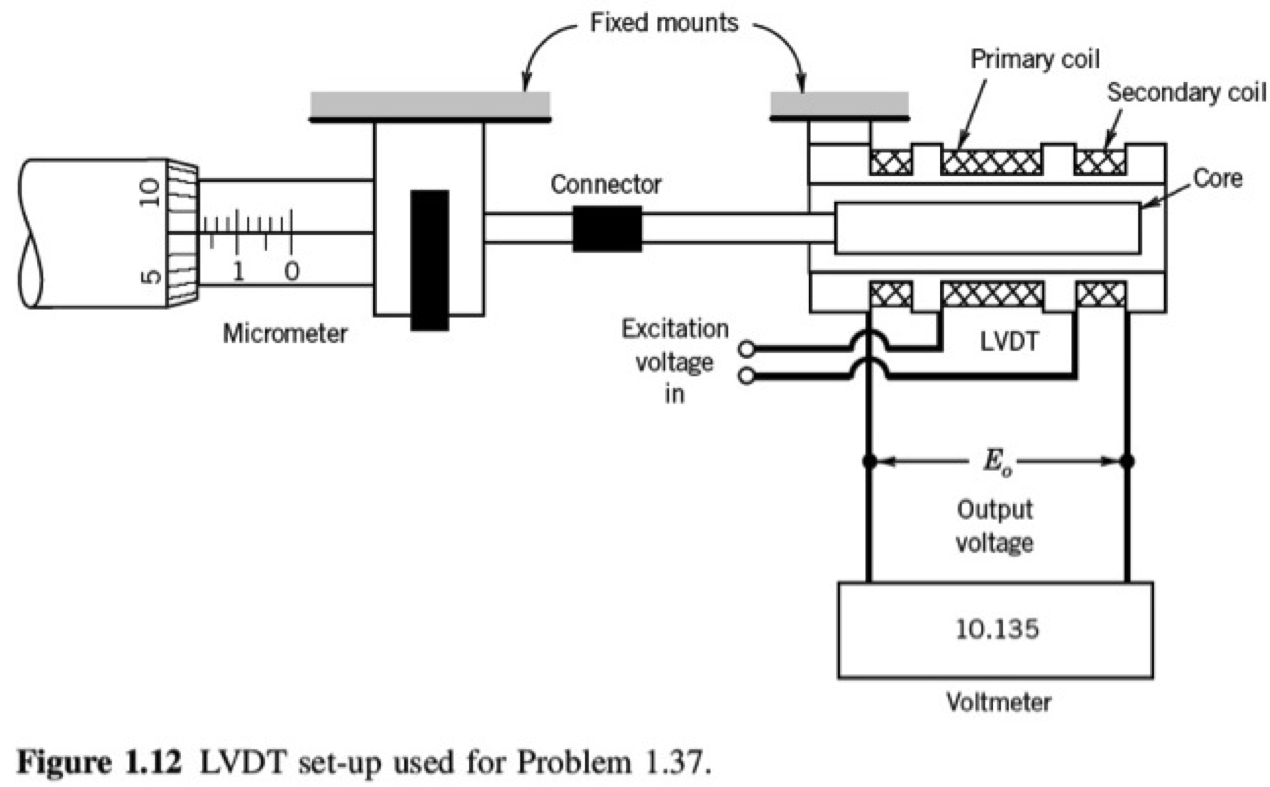
An engineer wants to calibrate the LVDT tool, using micrometer. The system looks like this:
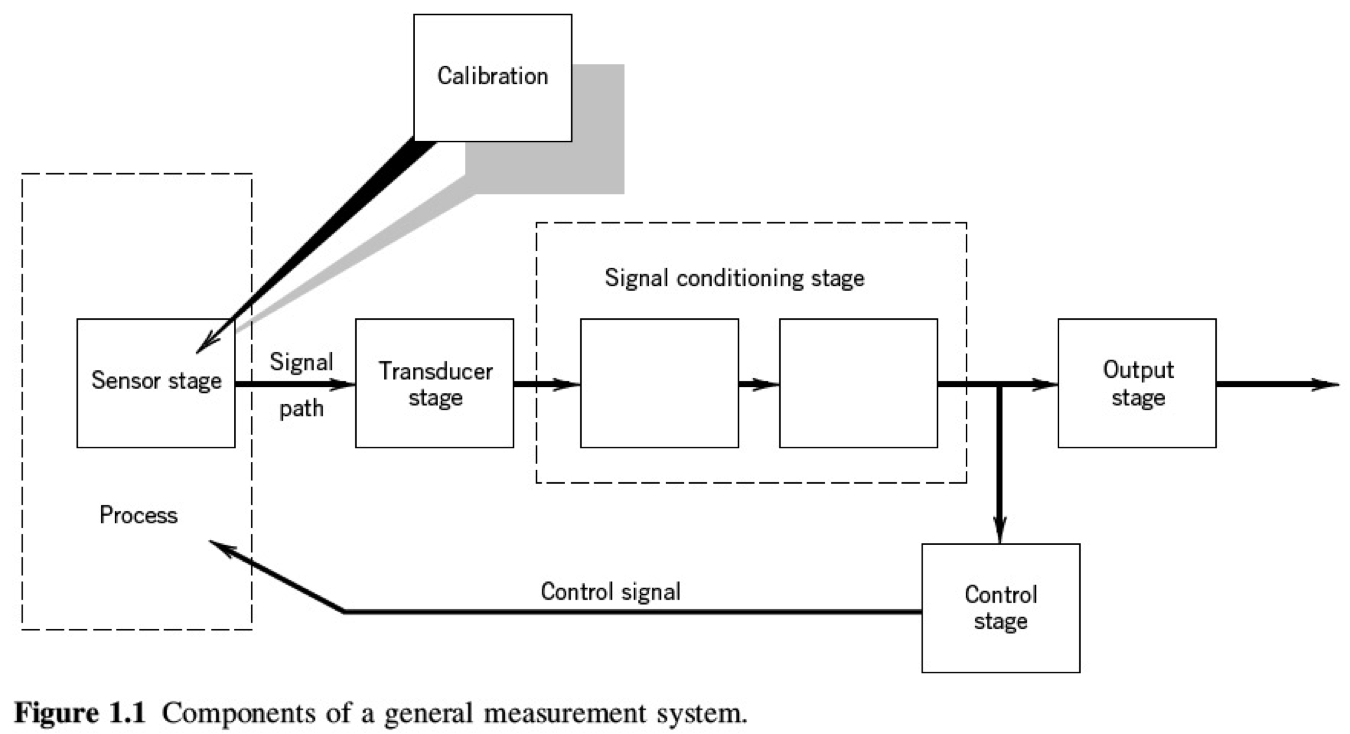
Please, describe the system according to the general system scheme:
what is the sensor in Figure 1.12?
what is the signal of the sensor output ?
what is the transducer?
what is the signal after transducer?
what kind of signal conditioning the LVDT does?
what kind of output there is after the system?
is there a feedback?
Question 2#
Calibration and regression
Each group runs the notebook to get their own original set of data in terms of two arrays (at least 5-6 samples long): concentration \(c\) (in particles per million, ppm) versus transmissivity \(T\) (in percents, 100% is completely transparent, i.e. clear water): LINK (** use Cell -> Run All **)
This is a calibration data, the process temperature depends on the concentration. Plot the data \(c = f(T)\)
Find the sensitivity, the input range, the output range (full scale output) and the relevant errors.
Find out what would be the concentration if in the experiment we measure \(T = 35.6\%\)