Signal construction and helper functions for the frequency content class#
import numpy as np
from scipy import fft
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def create_signal(fs,N):
""" create a secret periodic signal with a Gaussian noise"""
dt = 1./fs
t = np.linspace(0,N*dt,N)
y = 3.0+3.0*np.sin(2*np.pi*10*t)+1.2*np.sin(2*np.pi*24*t) # this is a secret function
noise = np.random.normal(0,1,N)
y += noise
return t, y
def spectrum(y,Fs):
"""
Plots a Single-Sided Amplitude Spectrum of a sampled
signal y(t), sampling frequency Fs (lenght of a signal
provides the number of samples recorded)
Following: http://goo.gl/wRoUn
"""
n = len(y) # length of the signal
k = np.arange(n)
T = n/Fs
frq = k/T # two sides frequency range
frq = frq[range(np.int(n/2))] # one side frequency range
Y = 2*fft(y)/n # fft computing and normalization
Y = Y[range(np.int(n/2))]
return (frq, Y)
def plotSignal(t,y,fs):
""" plots the time signal Y(t) and the
frequency spectrum Y(fs), after removing
the DC component, Y.mean()
Inputs:
t - time signal, [sec]
Y - values, [Volt]
fs - sampling frequency, [Hz]
Outputs:
plot with two subplots: y(t) and the spectrum Y(f)
Usage:
fs = 30, N = 256
t,y = create_signal(fs,N)
plotSignal(t,y,fs,N)
"""
# t,y = create_signal(fs,N)
y = y - y.mean()
frq,Y = spectrum(y,fs)
# Plot
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(2,1,1)
plt.plot(t,y,'b-')
plt.xlabel('$t$ [s]')
plt.ylabel('$Y$ [V]')
# axes().set_aspect(0.2)
# title('sampled signal')
plt.subplot(2,1,2)
plt.plot(frq,abs(Y),'r') # plotting the spectrum
plt.xlabel('$f$ (Hz)')
plt.ylabel('$|Y(f)|$')
def sampling(t,y,fs):
""" sampling of a signal y(t) at frequency fs [Hz]
inputs:
t - time signal [s], array of floats, dense sampled
y - signal [Volt], array of floats
fs - sampling frequency [Hz], float
"""
dt = 1./fs
ts = np.arange(t[0],t[-1],dt)
# ts = np.linspace(t[0],t[-1],(t[-1]-t[0])/dt)
ys = np.interp(ts,t,y,left=0.0,right=0.0)
return ts,ys
def quantization(ys,N):
"""quantization of a signal
inputs:
ts - time signal [s], array
ys - signal [Volt], array
N - number of bits, scalar (2,4,8,12,...)
outputs:
yq - digitized signal at N bits
"""
#quantization
# N = 4 # number of bits
max_value = 2**(N-1) - 1
yq = (ys*(max_value)).astype(np.int32)/(max_value)
return yq
def clipping(y,miny=-5,maxy=5):
""" clipping of signal
inputs:
y - signal [V] array of floats
miny, maxy - lowest, highest values [V], scalar floats, default -5 ..+5 [Volt]
outputs:
y - clipped signal [V]
better use: numpy.clip
"""
y[y < miny] = miny
y[y > maxy] = maxy
return y
def find_nearest(array, values):
index = np.abs(np.subtract.outer(array, values)).argmin(0)
return array[index]
# sample and hold
from scipy.interpolate import interp1d
def adc(t,y,fs=1.,N=4,miny=-5.,maxy=5.,method=None):
""" A/D conversion
Inputs:
t - time [s] array of floats,
y - signal [V] array of floats,
fs - sampling frequency [Hz], scalar float,
N - number of bits of the A/D converter, (2,4,8,12,14,...)
miny, maxy - lowest, highest values [V], scalar floats, default -5 ..+5 [Volt]
method - the reconstruction method: 'zoh' = zero-and-hold, 'soh' - sample and hold or None
outputs:
ts - sampled times [s]
yq - sampled and digitized signal [V]
yr - reconstructed, sample-and-hold signal [V]
Usage:
t = np.linspace(0,10, 10000)
y = 5+np.sin(2*np.pi*1*t)
ts,yq,yr = adc(t,y,fs=4,N=14,miny=0,maxy=10) # monopolar
plt.figure()
plt.plot(t,y,'k--',lw=0.1)
plt.plot(ts,yq,'ro')
plt.plot(t, yr,'b-')
"""
# first sample
ts,ys = sampling(t,y,fs)
# clipping
ys = clipping(ys,miny,maxy)
# digitize
yq = quantization(ys,N)
# sample and hold reconstruction
if method == 'soh':
tr = t
soh = interp1d(ts, yq, kind='zero', bounds_error=False,fill_value=yq[-1])
yr = soh(tr)
elif method == 'zoh':
tr = t
yr = np.zeros_like(tr)
index = np.abs(np.subtract.outer(tr, ts)).argmin(0)
yr[index] = yq
elif method is None:
tr = ts
yr = yq
else:
raise(ValueError)
return ts,yq,tr,yr
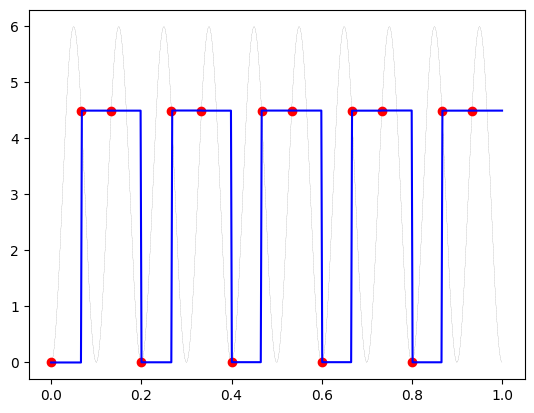
# example
t = np.linspace(0,1.,500)
y = 3+3*np.sin(2*np.pi*10*t-np.pi/2.)
ts,yq,tr,yr = adc(t,y,fs=15,N=12,miny=0,maxy=10,method='soh') # monopolar
plt.figure()
plt.plot(t,y,'k--',lw=0.1)
plt.plot(ts,yq,'ro')
plt.plot(tr, yr,'b-')
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x78edc06994c0>]